30 Interesting Unknown Facts About The Indian Constitution
30 Interesting Unknown Facts About The Indian Constitution

1) The Constitution Of India was ready to be burned ?

- The Father Of The Indian Constitution , Dr. B. R. Ambedkar , said that if he finds the Constitution to be misused then he will be the first to burn it as he didn't wanted the Constitution since it doesn't suits anyone , further he even said that the greatest harm will come by ignoring minorities.
2) Why is the Constitution of India created ?

- Constitution Of India is created to Establish a Government in India by facilitating the power of Sovereignty from the British Empire to the Indian hands.
3) The Constitution Of India was completely hand written by Prem Behari Narain Raizada.
- It was handwritten by Prem Behari Narain Raizada in a flowing Italic Style within 6 Months. 254 pen-holder nobs were used of Nibs No. 303
4) Each Page of the Indian Constitution was decorated and calligraphed
- Now this task of accomplishing the Indian Constitution with fine arts was handed over to Acharya Nandalal Bose in Kala Bhawan , Shantiniketan along with his students.
- Nandalal Bose painted the pages himself and guided his students in designing for other art works .
5) The Constitution of India was originally written in Hindi and English.

- Each member of the Constitution of India used two sign two copies of Constitution , i.e , one in Hindi and one in English
6) The Indian Constitution took 3 years to be written.

- The Constitution of India took 3 years to be completed consisting of 232 Pages .
7) The English Version consists of 117,369 Words.

8) The Constitution Of India is the longest written Constitution in the World
- It is the longest one with 25 parts containing 448 Articles and 12 Schedules . Up till now it has gone through a total of 101 Amendments .
9) Original Copies of The Indian Constitution are stored in the Library of the Parliament of India
- Original Copies of the India Constitution is kept in a helium filled case present in the Library of The Parliament of India .The illustrations present in it represents different civilizations with different styles depicting from the prehistoric times to the present .
10)The Indian Constitution declares India a Sovereign , Democratic Republic , Socialist , Secular
- The Constituent Assembly adopted " Enact And Give To Ourselves This Constitution " on 26 November 1949.
11) The Indian Constitution Assures Justice , Equality , Fraternity , Liberty to it's citizens

- Justice , Equality , Fraternity , Liberty are the 4 pillars of the Preamble of The Constitution Of India declaring equality to all citizens and maintain unity . This was adopted on 26 November 1949.
12 ) For the First time , The Constitution Assembly met on 9 December , 1946 .

- The first meeting of the Constitution Assembly was held in New Delhi , in the Central Hall of the Parliament House at Eleven of the Clock . The Constituent Assembly was formed on the recommendation of the Cabinet Mission which arrived at 1946 .
13 ) The First Draft were made to 2,000 Amendments .

- The "All Important Drafting Committee" which was directed to bore the responsibility of Drafting Constitutional documents was formed on 29 August , 1947 consisting of members : Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar , Diwan Bahadur Sir Narasimha Gopalaswami Ayyangar , K.M. Munshi , Sir Syed Mohammad Saadulla , N. Madhav Rao , D.P Khaitan & T Krishnamachari .
14) The Final Draft was ready on 26 November 1949

- It took 2 Years 11 Months and 18 Days to come up with the Final Draft . For the Final Draft the Assembly passed around 2473 Amendments out of 7635 tabled
15) The Indian Constitution was signed on 24 January 1950.
- The Indian Constitution was signed on 24 January 1950 by 284 members of the Constituent Assembly, which included 15 women . It came in to force two days after signing the Constitution.
16) The Indian Constitution was Legally Enforced of 26 January 1950
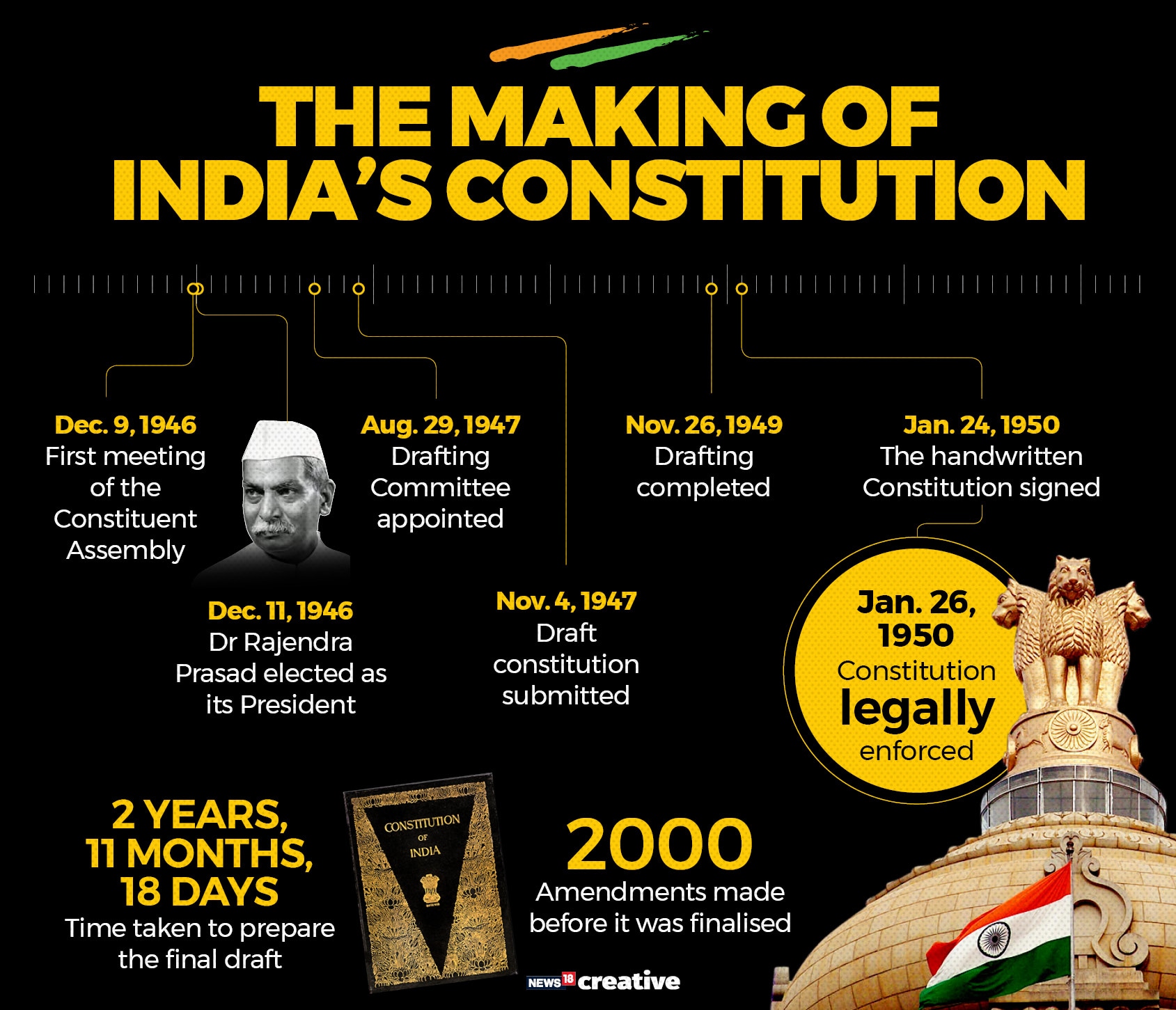
- 26 January was chosen for full legal Enforcement of The Constitution Of India as the date of complete Independence ( Purna Swaraj ) . The day of 26 January has its own importance in Indian history in the freedom for struggle of India .
17) The National Emblem Was Adopted on 26 January 1950

- The National Emblem of India , The LION , capital of Ashoka at Sarnath was adopted on the same day when the Constitution of India came into effect , i.e , on 26 January 1950 . The National Emblem consists of 4 lions among which only 3 are visible but the fourth one is hidden from the view . The symbol represents as a distinctive badge of nation depicting the power of Courage , Peace , Power , Confidence .
18) The Constitution Of India is often called as " A Bag of Borrowings " .

- The Constitution of India is much likely a combination of Constitutions with provisions of different countries , as no one holds any patent authorization for possessing the fundamental ideas of the Constitution , where , the main source of the Constitution of India is from the Constitution of Japan .
19) Fundamental Law of India was embodied on a series of statutes enacted by the British Parliament

- There are 5 division of law : Civil Law , Common Law , Customary Law , Religious Law & Mixed Law . Up till 2017 there were 1,248 laws but as per the Central Law also being State Law its difficult to calculate the exact number of law .
20 The Constitution consists Of India of some words Borrowed from the French Constitution.

- The words like Liberty , Fraternity , Equality and the concept of " Republic "are adopted from the French Constitution .
21) The Constitution of India consists of some words Borrowed from the USSR and Japan
- The concept of FYP ( Five Year Plan ) was taken from the USSR withe the concept ideas of Fundamental duties as well as the idea of Justice .
22) Borrowing from Weimar Constitution of Germany
- Concept of suspending The Fundamental Rights during Emergency was adapted from the Weimar Constitution of Germany .
23) The Basic Structure of the Indian Constitution stands on the Government of India Act , 1935
- Basically this Act , containing 321 Sections with 10 Schedules started a new system of " diarchy " , where the specific areas of the Government will be supervised by the Ministers ,i.e , like Education , Transportation , Finance , Health .
24) The Indian Constitution has been hailed as one of the World's Best Constitution.
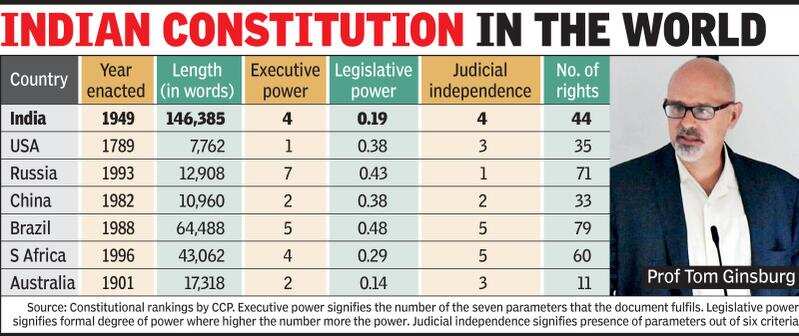
- The Constitution Of India is the longest in the world among any Sovereign countries with a total 117,369 words is established with an integrated diverse nation and is the leader in the Constitutional Amendments .
25) Adding the Concept of Preamble to The Indian Constitution
- Concept of Preamble to the Constitution of India is introduced by the Preamble of United States Of America which also starts with " We The People " .
26) "Right to Property" was one of the Fundamental Rights of the Indian Constitution

- The "Right To Property" , was also a part of Fundamental Rights . The Article 31 of our Indian Constitution said that " No person shall be deprived of his property saved by the Authority of Law". In 1978 the 44th Amendment Act removed it .
27) The Indian Constitution combines Rigidity and Flexibility :
- The Constitution of India is a mixture of both Rigidity and Flexibility since the Constitution providing the Federal structure of India makes the procedure of Amendment neither easy nor difficult . Thus a majority of two-third ( 2/3 ) of the Union Parliament is required to Amend the Constitution .
28) Six Fundamental Rights of the Constitution of India :

i) Right To Equality : There will be no partiality before the law based on : sex , caste , creed , religion , place of birth , disgrace.
ii) Right To Freedom : It provides us the Right to freedom of Speech , expression , association , movements , cooperatives , profession , exploitation
iii) Right To Freedom of Religion : Right to change his/her religion , to run his/her religious affairs and giving advice related particular community or institution.
iv) Right Against Exploitation : Right to banning of Forced Labor , Child Labor , misuse of services by force , human trafficking .
v) Right To Cultural And Educational Rights : Right for the citizen of any section to choose education , language , culture . establishing minorities to the educational institutes
vi) Right To Constitutional Remedy : Right to empower the citizens to move to courts in case of any denial or misuse or being not secure of their fundamental rights like threatening of his/her existence
29) Constitution of India provides a number of Directive Principles

- The Directive Principles are the guidelines provided to the federal Instituted that are governing/ruling the State of India . There are 20 Directive Principles present in the part IV of the Constitution of India .
30) Sanction of Single citizenship in the Constitution of India

- The Citizenship Act of 1955 provided the benefit of Single citizenship to the people in India stating that the People Of India cannot have the citize nship of any other country and there won't be any citizenship according to State .


Awsm research brother
ReplyDeleteKeep going